We unleash your business potential by maximize the business innovation.
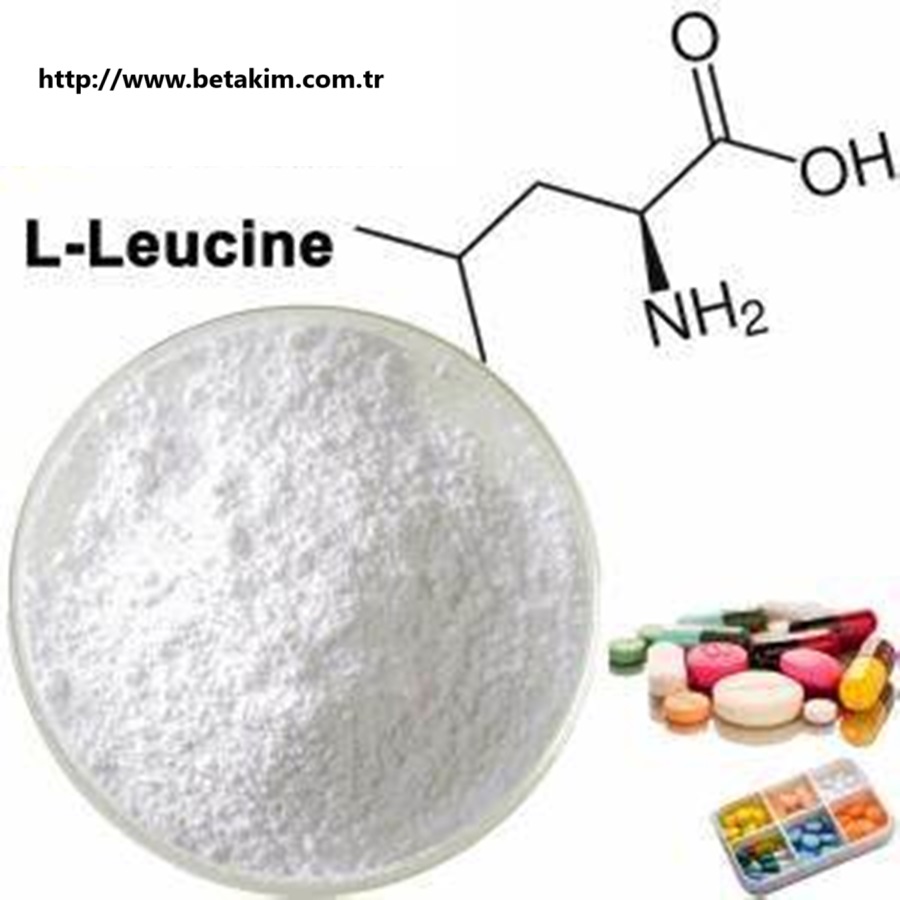
Send EmailL-Leucine, Leucine, 61-90-5
L-Leucine – Product Profile
Chemical and Physical Properties
-
Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₃NO₂
-
Molecular Weight: 131.17 g/mol
-
CAS Number: 61-90-5
-
Appearance: White crystalline powder
-
Solubility: Sparingly soluble in water (22 g/L at 25 °C); insoluble in ethanol and ether
-
Melting Point: ~293 °C (decomposition)
-
Density: 1.23 g/cm³ (approximate)
Applications
-
Sports Nutrition & Supplements:
-
Key component of BCAA blends (with isoleucine and valine).
-
Stimulates muscle protein synthesis via the mTOR pathway.
-
Supports recovery and lean muscle growth.
-
-
Dietary Supplements:
-
Found in protein powders, amino acid blends, and fortified foods.
-
Used in formulations for athletes and individuals with protein-deficient diets.
-
-
Medical Applications:
-
Studied for use in liver disease, muscle wasting conditions (sarcopenia, cachexia).
-
May support glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
-
-
Food Industry:
-
Incorporated into functional foods, protein bars, and sports beverages.
-
-
Research & Biochemistry:
-
Used in amino acid metabolism studies and protein synthesis research.
-
Synonyms and Other Names
-
L-Leucine
-
Leucine
-
2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
-
(S)-α-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
-
L-α-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
-
Essential branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)
Common Terms:
-
“Muscle-building amino acid”
-
“Athlete’s amino acid”
Biological Notes
-
Essential amino acid: Cannot be synthesized by the human body; must be obtained from diet.
-
Role in protein synthesis: Acts as a trigger for muscle growth by activating the mTOR signaling pathway.
-
Hydrophobic and aliphatic: Important for protein folding and stability.
-
Part of BCAA group: Alongside isoleucine and valine, forms the branched-chain amino acids critical for muscle metabolism.
Summary
L-Leucine (CAS 61-90-5) is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and plays a central role in muscle protein synthesis, recovery, and energy metabolism. It is widely used in sports nutrition, dietary supplements, medical research, and functional foods. Among the BCAAs, leucine is considered the most potent stimulator of muscle growth.
L-Leucine – Sectoral Suitability Table
| Sector | Application Purpose | Suitability | Notes / Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sports Nutrition & Supplements | Triggers protein synthesis, supports muscle growth and recovery | ✅ High suitability | Most critical BCAA; often used in high-leucine formulas (e.g., 4:1:1 ratios) |
| Dietary Supplements | Protein powders, amino acid blends, functional foods | ⚠️ Moderate suitability | Health claims must comply with regulations |
| Medical Applications | Liver disease, muscle wasting, metabolic research | ⚠️ Limited suitability | Requires GMP-grade purity and clinical oversight |
| Functional Foods | Sports drinks, protein bars, fortified foods | ⚠️ Moderate suitability | Labeling and claims must follow food law |
| Animal Nutrition | Growth and performance support | ❌ Low suitability | Rarely used; cost and regulation limit adoption |
| Industrial Chemicals / R&D | Amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis studies | ⚠️ Moderate suitability | Primarily for laboratory and academic research |
| Cosmetics | Anti-aging and skin recovery potential (experimental) | ❌ Low suitability | Still at research stage; not common in mainstream cosmetics |
Summary
L-Leucine (CAS 61-90-5) is the most potent BCAA for stimulating muscle protein synthesis. It is widely used in sports nutrition and supplements, with secondary applications in dietary products and medical research. Its commercial strength lies in muscle growth, recovery, and metabolic regulation.