We unleash your business potential by maximize the business innovation.
Send EmailCorrosion Inhibitor, Anodic Inhibitor, Cathodic Inhibitor, Mixed Inhibitor, Film-Forming Inhibitor
What is a Corrosion Inhibitor?
Corrosion inhibitors can be classified in several different ways, depending on the type of metal and the environment in which they are used. The main types of corrosion inhibitors are:
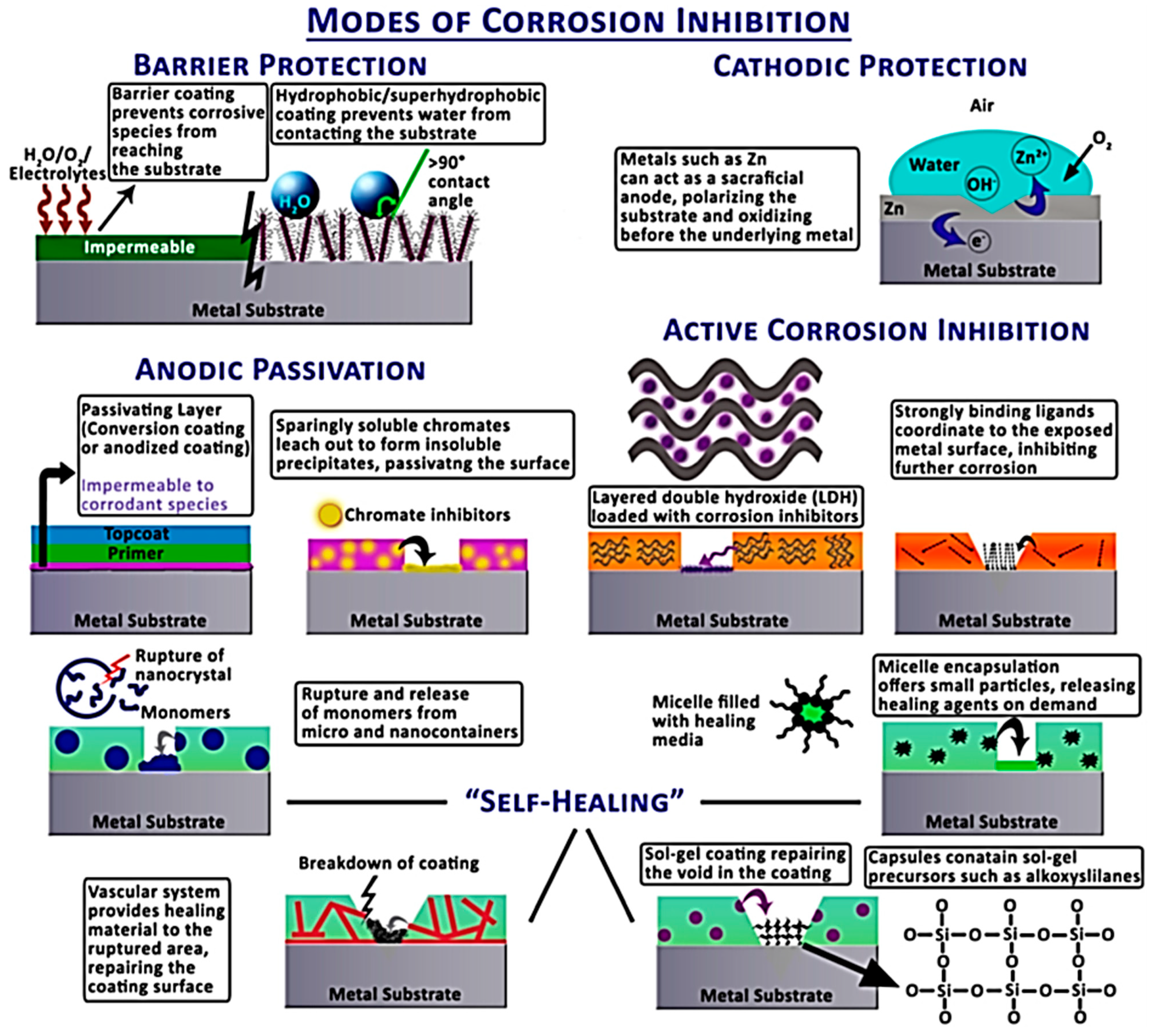
Anodic Inhibitors: These inhibitors interact with the anodic region of the metal by slowing down the corrosion process. They usually form a protective film on oxidizable metal surfaces. The most common anodic inhibitors are chromates, molybdates and phosphates.
Cathodic Inhibitors: Cathodic inhibitors act in the cathodic regions of corrosion cells by reducing the corrosion current. These inhibitors work by preventing the formation of hydrogen gas on the metal surface. The main cathodic inhibitors are zinc, calcium and magnesium salts.
Mixed Inhibitors: These inhibitors are effective in both anodic and cathodic areas. They form a general protective film on the metal surface that prevents corrosion. Carboxylates and organic amines are included in this group.
Oxygen Inhibitors: Most of the time, the presence of oxygen accelerates corrosion. Corrosion is prevented by oxygen inhibitors by chemically binding dissolved oxygen in water. Commonly used oxygen inhibitors are sodium sulfate and hydrazine.
Film-Forming Inhibitors: The purpose of these inhibitors is to form a protective thin film layer by preventing direct contact between the metal and its environment. This slows or stops the corrosion process. Film-forming inhibitors commonly include organophosphorus compounds and organic amines.
What are Corrosion Inhibitors?
All types and methods used in metal structures and equipment for corrosion prevention. They can be used with or without corrosion inhibitors. The main corrosion protection methods and materials are:
Coatings: A common way to prevent corrosion is to cover metal surfaces with protective coatings. These coatings interrupt corrosion by preventing contact between the metal and its environment. Metal surfaces are usually protected with paints, varnishes, epoxy coatings and powder coatings.
Galvanization: The process of coating steel and iron surfaces with zinc is called galvanization. Zinc protects iron and steel surfaces before corrosion begins. Metal structures used in outdoor and harsh environmental conditions are protected by galvanization.
Cathodic Protection: In this method, corrosion is prevented by turning the metal surface into a cathode. Cathodic protection is applied with two main methods: applied current protection and galvanic anode protection. These methods are used in pipelines, tanks and large metal structures.
Anodic Protection: Anodic protection slows down the corrosion process by making the surface function as an anode. It is frequently used to protect stainless steel and other alloys.
Usage with Corrosion Inhibitors: When the physical methods mentioned above are combined with chemical corrosion inhibitors, they provide greater effectiveness in terms of physical protection. For example, when the metal surface is painted and the inhibitor is added at the same time, versatile protection is provided.
Material Selection: The first step in corrosion prevention is to select corrosion-resistant materials. Corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, titanium and alloyed metals are used in critical applications.
Environmental Control: It is important to control environmental conditions to slow down the corrosion process. Methods such as humidity control, oxygen reduction or removal of corrosive substances from the environment are applied.
Extending the life of metal structures and equipment relies on corrosion inhibitors and corrosion prevention methods. Corrosion weakens metal surfaces, jeopardizes structural integrity and increases safety risks. Therefore, corrosion control is of critical importance to ensure the efficient and safe operation of industrial processes, infrastructures and equipment.
Direct chemical action is also provided by corrosion inhibitors to protect metal surfaces. In fact, various types of inhibitors are available, such as anodic, cathodic inhibitors, film-forming inhibitors and oxygen inhibitors, and the protection obtained is usually comprehensive. Corrosion prevention techniques such as coatings, galvanization, cathodic protection and material selection provide both physical and chemical protection to metal surfaces at the same time.
For successful corrosion control, the right inhibitors and prevention methods must be selected. It is important to make this choice according to the environments where metal surfaces are exposed to certain conditions and corrosion mechanisms. With appropriate applications, metal structures will have a longer life, less costly maintenance and can operate safely.